Chillers for nuclear power plants
Introduction
Chillers are used everywhere in the industry where it is necessary to cool something. Be it in industry, buildings or even nuclear power plants. In the nuclear industry, however, the safety requirements are many times higher. Depending on the area of application, the machines must also function in critical situations, e.g. an earthquake, a tsunami or a plane crash.
After Chernobyl and Fukushima, the requirements regarding earthquake loads were again drastically tightened.
Since Merkle & Partner has carried out various verifications in nuclear plants and reinforcement measures based on simulation results are included in the design, it was obvious that the development of a new chiller should also be carried out by our company as part of a pilot project.
The design and the computational verification were carried out for the company Cofely Refrigeration GmbH, the end customer was the French Areva Group.
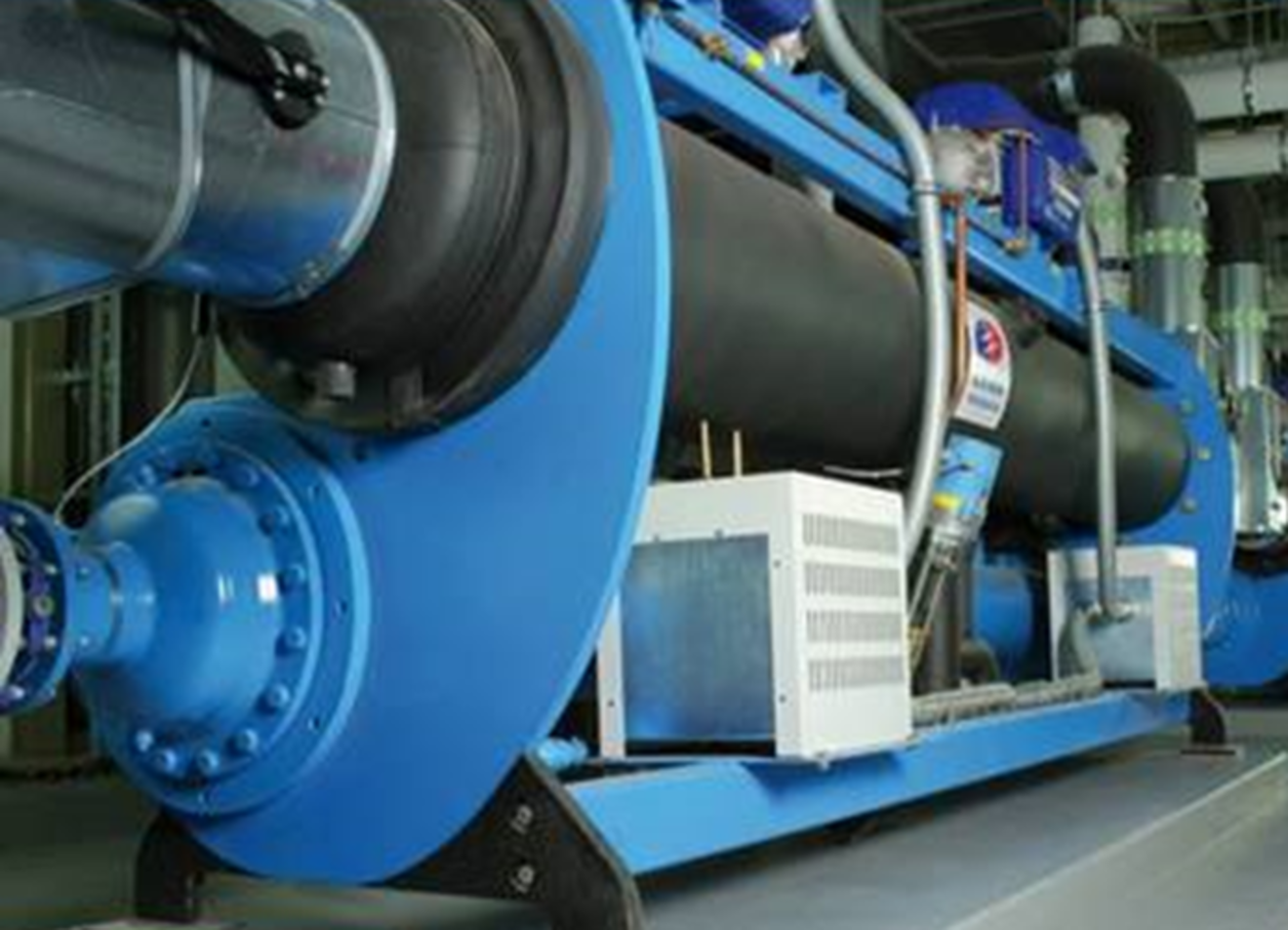
The machines are used in the Flamanville nuclear power plant.
Task / Calculation
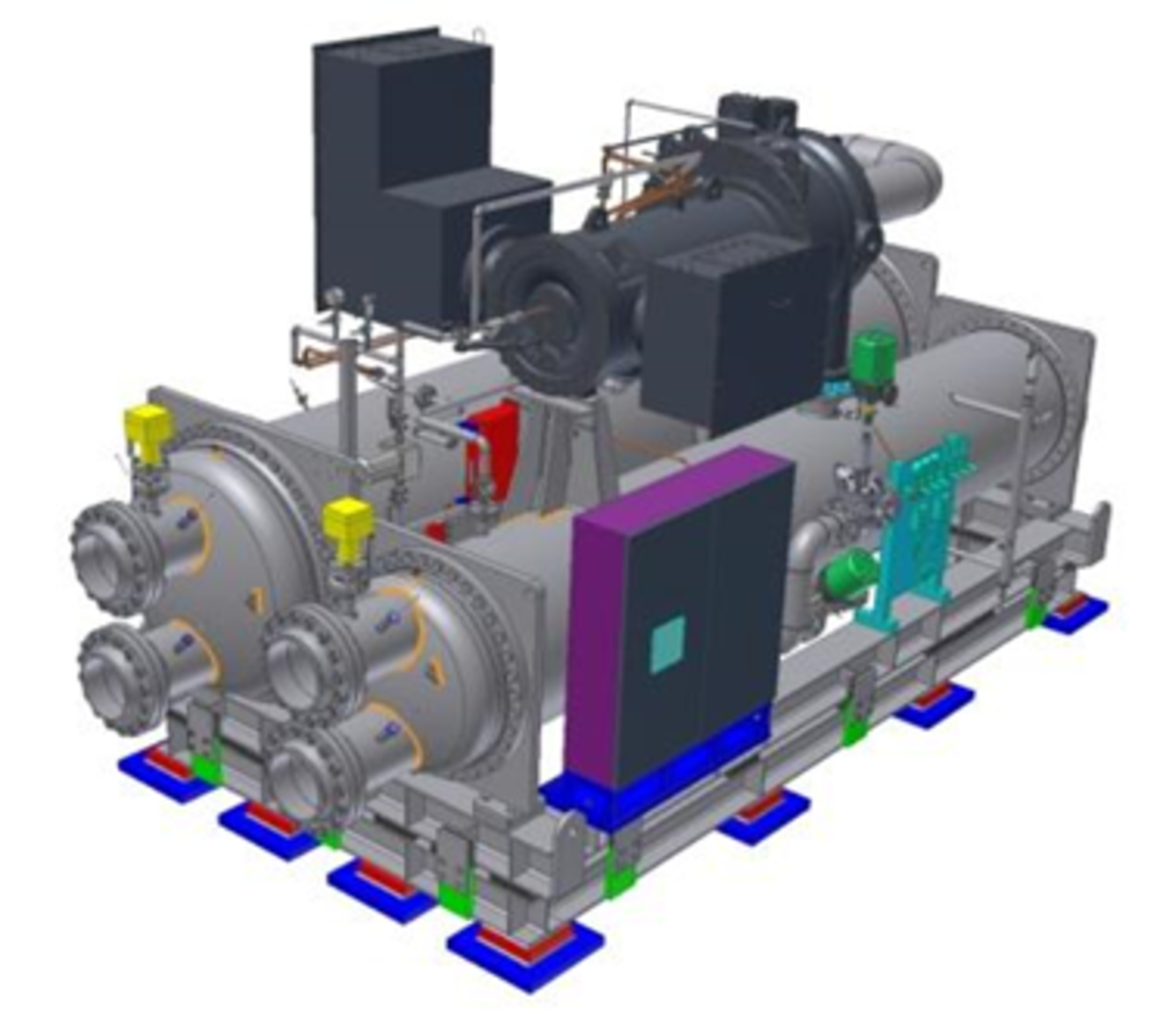
The packaging and the components to be used, such as compressors, condensers and control cabinets, were specified in this case. The dominant load cases were earthquake load cases, where the corresponding standards were drastically tightened in the course of the project.
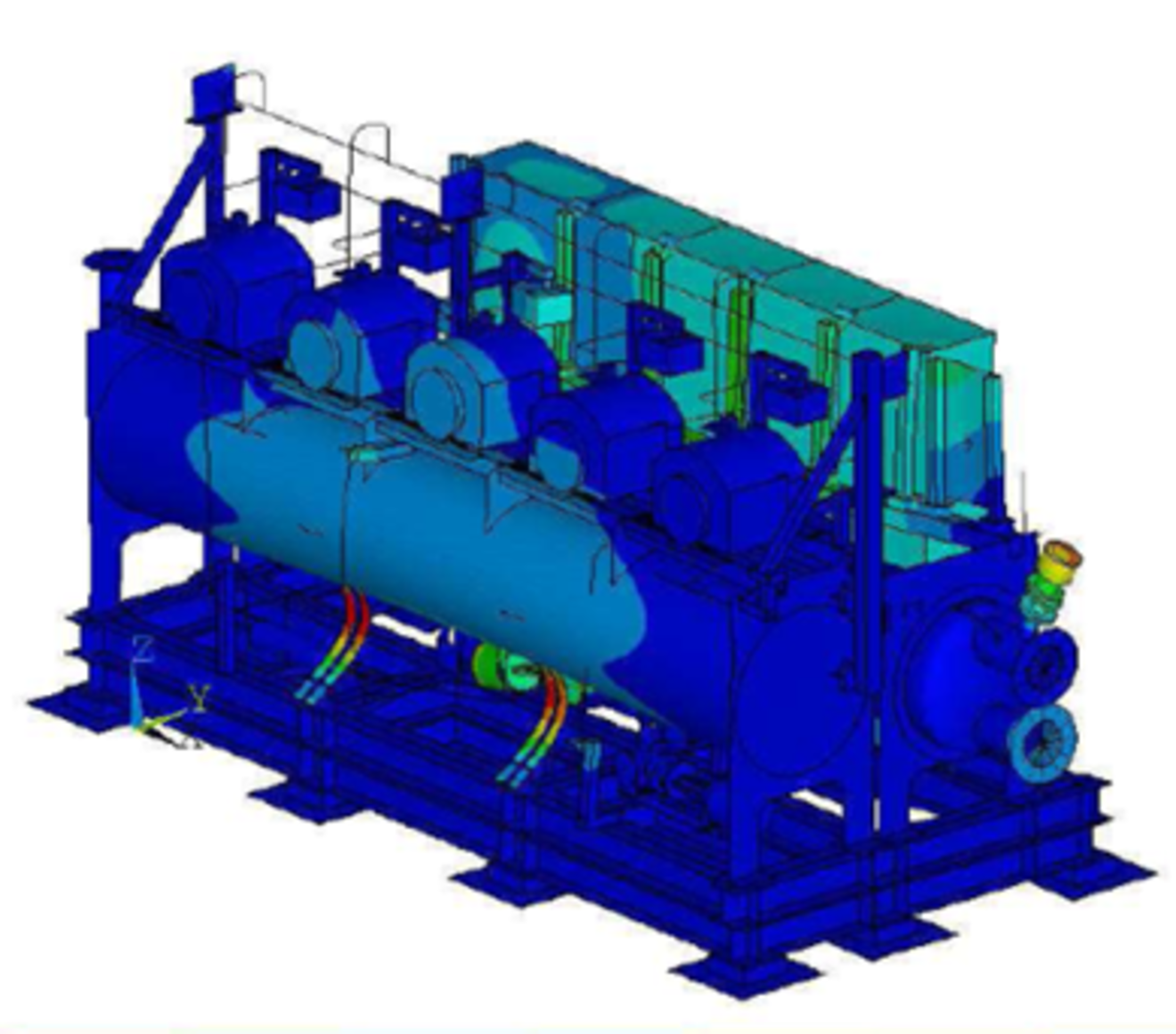
The dimensioning of the frame, the struts and the bolted connection was carried out on the basis of finite element calculations in accordance with the relevant standards.
The documentation effort, especially with the tightening regulations, was considerable. New requirements had to be endured and taken into account again and again.
Results
The proof for the design could also be provided in consideration of the increased requirements. In the course of several follow-up projects, Merkle & Partner acquired extensive know-how especially in this highly safety-relevant area.
Outlook
Even after Germany's hasty exit from nuclear energy, nuclear power plants continue to be built around the world.
China alone planned 44 nuclear reactors in 2020, which will be commissioned over the following 8-10 years, followed by reactors in Russia and India. Despite Fukushima, Japan is also relying on nuclear power, as other ways to secure energy for the country have proven less than successful.
In 2019, 5 new nuclear power plants came online worldwide.